

Waves & Wave Phenomena (AHL)
Worksheet and answers
Class notes
Snell's circle Explanation


The boundary part

Gap is large compared to wavelength Gap is small compared to wavelength




Reason for interference pattern.
According to Huygen's principle, the gap can be seen to consist of many small individual wave sources (blinking points). The right side shows how the intensity of the waves hitting the right wall varies.
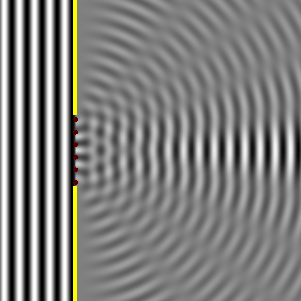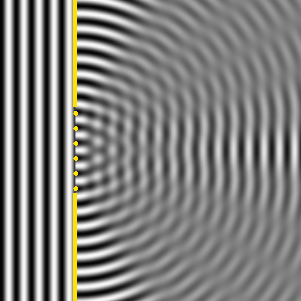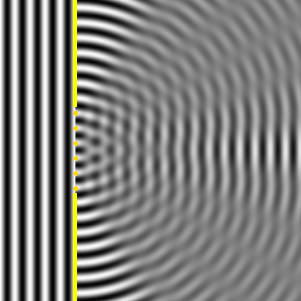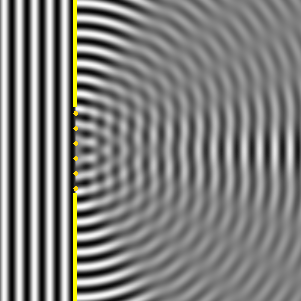

Figure 1 Figure 2
Same thing here. The blue area shows constructive interference, the green destructive. The constructive interference is strongest in the middle, hence the peak in intensity.


Angle of incidence is not 90° Angle of incidence is 90°


Explanation In glass fiber
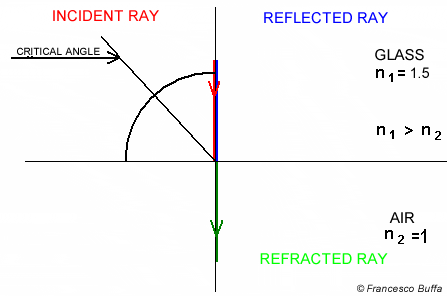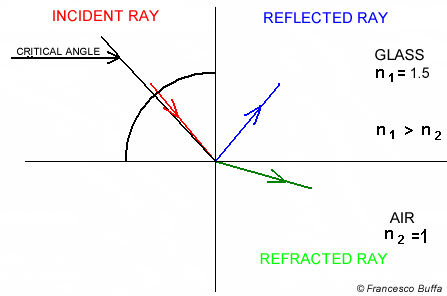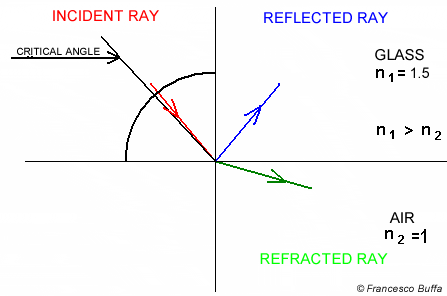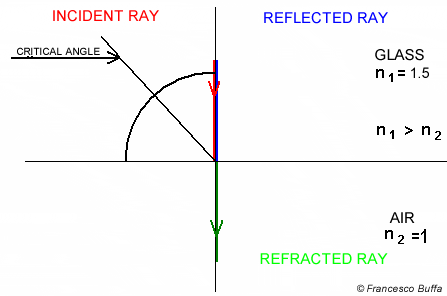

In water

Hard boundary Soft boundary


Plane polarized wave shown from two different angles.
The variation of the electric field is shown in red and the variation of the magnetic field is shown in blue


Stationary source Moving source


Speed of source = speed of wave Speed of source > speed of wave


Standing waves (different harmonics) Standing waves from travelling waves.


Standing longitudinal waves

Pulses in opposite direction Constructive and destructive interference


Superposition on a slinky
