

Waves
Cambridge
Assignments
Reflection

Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection
Refraction
Refraction is the change in direction of a wave when it transmits from one medium to another.

The angle of incidence and the angle of refraction can be determined by Snell’s law given by the following formula
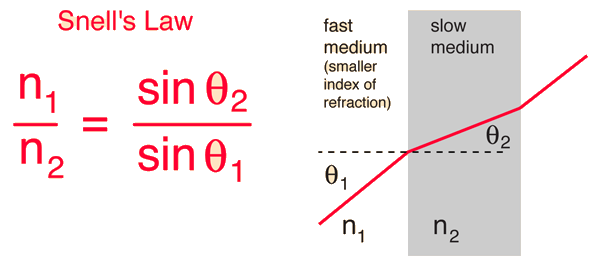
where n1 and n2 are the refractive indexes for their respective mediums


Fast-to-slow: towards normal; slow-to-fast: away from normal
In addition, the refractive index n1 and n2 are related by the following equation
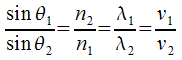
where v1 and v2 are the speed of the waves in their respective mediums and λ1 and λ2 are the wavelength of the waves of their respective mediums

Total Internal Reflection

The refractive index and the critical angle are related by the following equation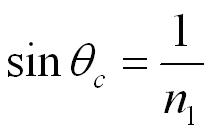 Total internal reflection only occurs when the light ray propagates from a optically denser medium to an optically less dense medium.
Total internal reflection only occurs when the light ray propagates from a optically denser medium to an optically less dense medium.
Diffraction
When waves pass through a gap in a barrier, they spread out into space beyond the barrier. This spreading of the waves is called diffraction.

The waves are diffracted the most when the width of the gap is similar to the wavelength of the waves.
(The effect is strongest in c and weakest in a)

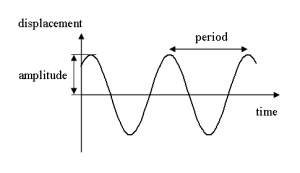
| Amplitude | Period (T) | Frequency (f) | ||
| Maximum displacement of the oscillating object | Time taken for one complete oscillation (in seconds) | Number of times the object oscillates per unit time (usually one second)
f=1/T |

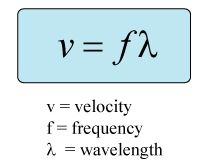
Wave speed can be calculated by the following equation
| Transverse wave | Longitudinal wave |
The direction of oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of the energy transfer
|
The direction of oscillation is parallel to the direction of the energy transfer |
| Example:
Water waves Wave in a string flicked up and down Light (electromagnetic waves) |
Example:
Wave produced in a spring Sound waves Earthquake P-waves |
| Transverse wave | Longitudinal wave |
| A point with maximum positive displacement is called a crest.
A point with minimum displacement is called a trough. |
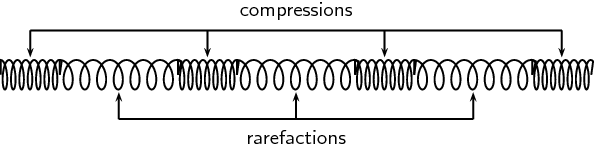
A region where particles are closed to each other is called a compression.
A region where particles are furthest apart from each other is called a rarefaction. |
 |
 |
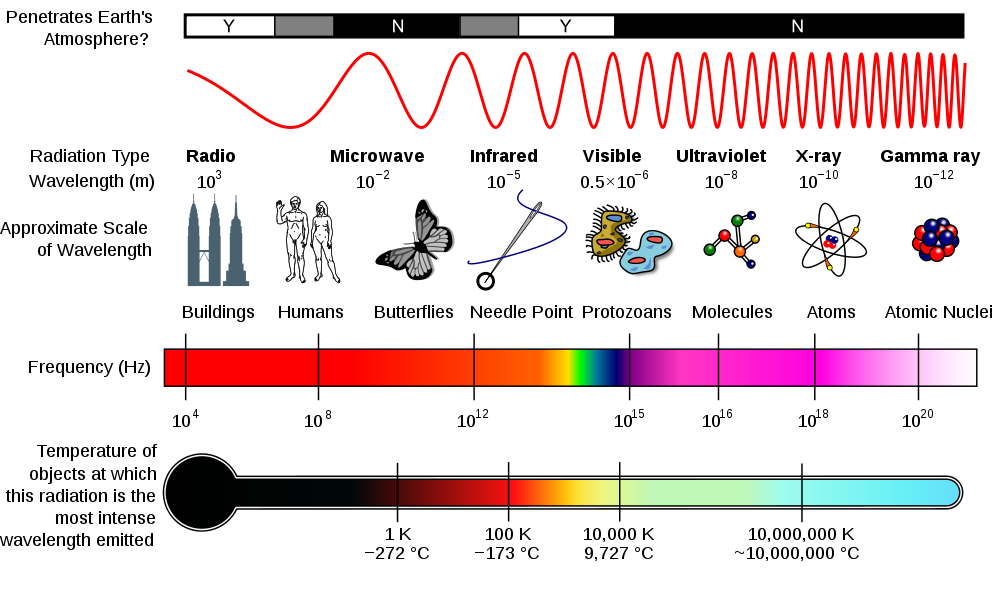
All EM waves travel in vacuum at the same speed of 3*10^8m/s.
EM waves are transverse waves.
The speed of sound in 20 degrees Celsius dry air is approximately 343.2m/s.
Sound waves are longitudinal waves.

Gap is large compared to wavelength Gap is small compared to wavelength




Explanation In glass fiber
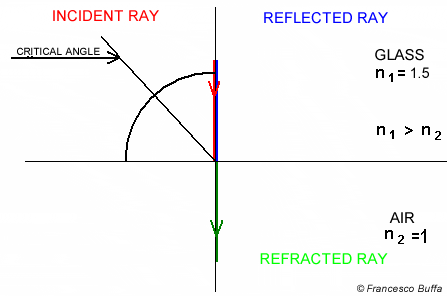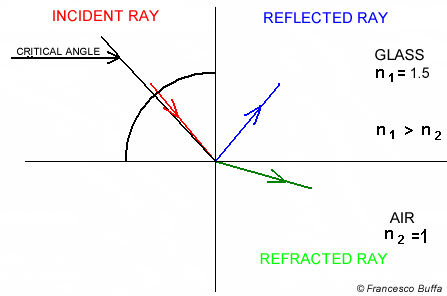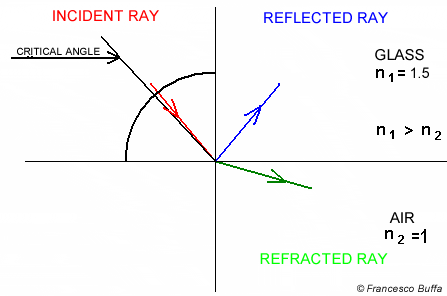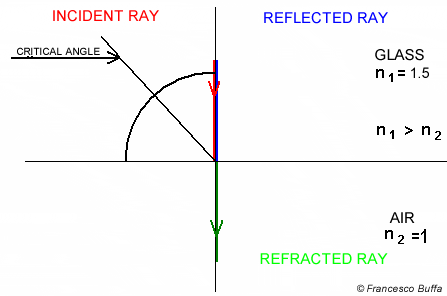

In water



Dispersion of light through a prism

Angle of incidence is not 90° Angle of incidence is 90°



Longitudinal Waves

Transverse waves

Water waves
