

C.3 Wave phenomena (+HL)
How does an increase in the index of refraction change the speed of the wave travel?
Wavelength and speed changes, but not frequency. How can you see that the frequency doesn't change?
Angle of incidence is not 90° Angle of incidence is 90°


Explanation In glass fiber
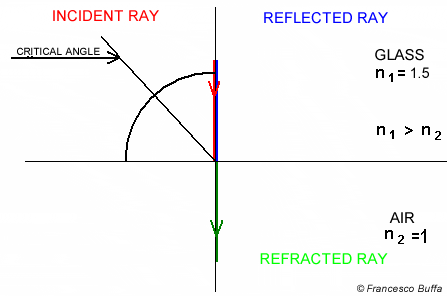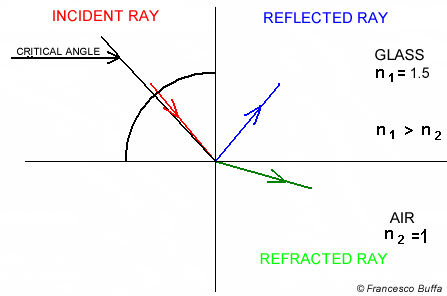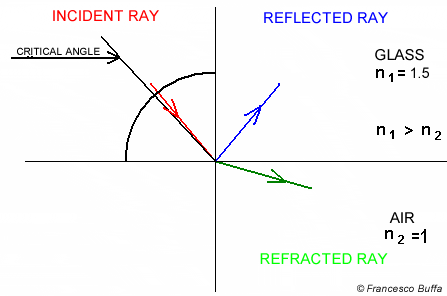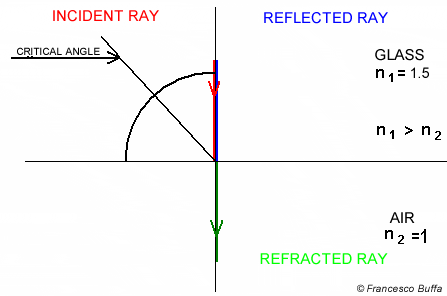

In water

Hard boundary (phase shift 180°) Soft boundary (no phase shift)


Around an obstacle Through a small slit. Through a circular aperture

 .
. 
Pulses in opposite direction Constructive and destructive interference Superposition on a slinky

 .
. 
The purple wave shows the sum of the red and the blue waves.
A) What kind of pattern do you observe? What is this pattern called?
B) Choose the pressure sensor on the right and move it to the right side of the box. Only use one of the sensors. Move it vertically on the right side of the screen.
C) Click "both" at the bottom right. Where do you have maximum compressions? Where do you have maximum rarefactions?
Choose Example: Two Sources, Waves = Sound, Colour Scheme: Your choice, Source frequency = 6
Although the source is sound, think of these waves as water waves. It gives you the same pattern.
Non coherent light will not form any pattern. The changes are too fast for the eye to observe. Coherent waves create a pattern on the screen



Set the following values: wavelength = 4, L = 100, and d = 20. Do not change these values.
nλ = d sinθ